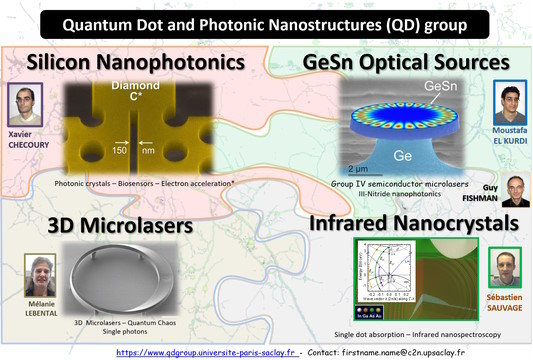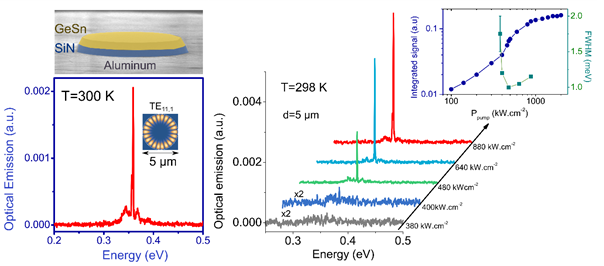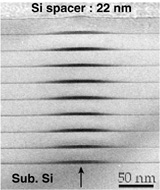
The Quantum Dot and Photonic Nanostructures group (QD for short) is a research group in the department of "Photonics" of Centre for Nanoscience and Nanotechnology.
↓ Highlight January 2022: First Room temperature GeSn laser published in Optics Express pdf ↓
(click the picture to open)
A large large part of the activity of the group focuses on photonic crystals which are designed, modeled, measured and fabricated by the team in the clean room facility of the Centre. We study in particular the enhancement of non-linear interactions in photonic crystal nanocavities made of silicon, diamond, germanium or nitride materials: Second harmonic generation, frequency tripling, Raman emission, auto-oscillations, two-photon absorption photodetection, biosensing etc. We also investigate light emission in tensile strained germanium to provide efficient optical sources for silicon photonics. The historical part of the activity is dedicated to the local control of photonic energy and the enhancement of the interaction between light (photons) and matter (electrons, phonons) at the smallest nanometric scales. We like looking at semiconductor nanostructures with strong electronic confinement like semiconductor
self-assembled quantum dots. Self-assembled quantum dots are
semiconductor nanostructures with characteristic dimensions in the
nanometer or tens of nanometers
scale. Self-assembled quantum dots can be formed spontaneously by
growing
lattice mismatched materials like InAs on GaAs or Ge on Si. The physics
and the potential applications of these nanostructures are incredibly
rich.
At the nanometer length scale, the motion of the carriers is governed
by
quantum mechanics and the energy levels are quantized just like atoms
or
molecules. From this point of view [of discrete energy levels],
self-assembled
quantum dots can be considered as artificial atoms inserted into a
solid
matrix. However this picture is limited. The coupling of the carriers
with
the environment like the vibration modes of the crystals, leads to very
specific properties and interaction mechanisms. We account for the electron-phonon interaction in semiconductor quantum dots which leads to the formation of polarons (entangled electron-phonon quasiparticule), in particular in the far infrared spectral range: time-resolved relaxation and decoherence dynamics, non-linearity like second and third harmonic generation, multiband k.p modelling of the electronic structure and infrared spectroscopy going from ensemble to single quantum dot measurements corresponding to a sub-wavelength ultrasensitive absorption nanospectroscopy instrumentation.
Semiconductor quantum dots are potential candidates for several type of
optoelectronic devices like long wavelength lasers or midinfrared
photodetectors with improved performances as compared to bulk or
two-dimensional heterostructures. They are also potential candidates
for quantum information processing
as single photon sources or support of qubits. Our group studies different materials in particular those related to InAs/GaAs quantum dots and
Ge/Si
self-assembled quantum dots :
See thepublications section (top bar) for an up-to-date overview of the activities.
Optical spectroscopy of nanostructures
Modeling of the electronic structure
of nanostructures
Single quantum dot absorption
nanospectroscopy
Photonic devices : semiconductor
quantum dots and photonic crystals
Quantum information processing
with quantum dots
Our group also develops optical telecommunication experiments related
to the saturable absorption properties of semiconductors :
Saturable absorption of low-dimensional semiconductors
To learn more about our studies, visit the research web page or click
on the links above.
The quantum dot group is part of the SANDiE european network of
excellence, that brings together 32 european leading groups in the
field of self-assembled semiconductor nanostructures.
Past events:

We have co-organized a Nanophysics day in the framework of Nanophysics pole of PhOM department of the University Paris-Saclay 19 October 2017: fanaphy.sciencesconf.org
Our group has co-organized JBQ 2013, a recurrent national event on quantum dots 24-25 june 2013: jbq2013.upmc.fr
We contribute to the organization of the international conference OECS12 12-16th septembre 2011: www.oecs12.org
Our group co-organizes JNMO 2010, a recurrent national event 28 setp.-1st oct. 2010: www.jnmo2010.org
SANDiE 1st Intersublevel Workshop 2-3 April 2008 Paris: http://www.QDgroup.universite-paris-saclay.fr/islworkshop/
SANDiE 2nd SanCharMod Workshop 12-13 December 2007 Paris: http://www.QDgroup.universite-paris-saclay.fr/SanCharMod/
Our group teaches in master "Components and Antenna for Telecommunications": M2 CAT at university Paris-Sud and contributes in "Quantum Mecanics" basic courses at ENSTA and Centrale-Supélec.

QD Group advisor: Dr Sebastien Sauvage -
Phone : +33 1 70 27 05 10
e-mail : sebastien.sauvage (at) c2n.upsaclay.fr
Up-up-level : Centre for Nanoscience
and Nanotechnology